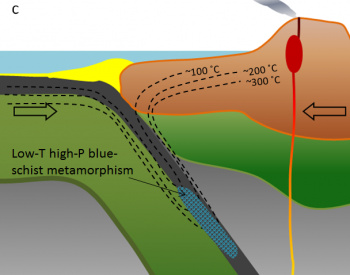
It turns into eclogite at about 35 km depth, and then eventually sinks deep into the mantle, never to be seen again. Cataclastic Gneiss usually is distinguished from schist by its foliation and schistosity; gneiss displays a well-developed foliation and a poorly developed schistosity and cleavage. So, if you get a chance to see this most beautiful rock in person, appreciate it for the treasure it is. [67], At the shallowest depths, a fault zone will be filled with various kinds of unconsolidated cataclastic rock, such as fault gouge or fault breccia. With increasing grade of metamorphism, further recrystallization produces foam texture, characterized by polygonal grains meeting at triple junctions, and then porphyroblastic texture, characterized by coarse, irregular grains, including some larger grains (porphyroblasts. WebCataclastic metamorphism is not very common and is restricted to a narrow zone along which the shearing occurred. How do you fix yellow leaves on a holly bush? c.) it occurs when a meteorite collides with Earth The force of the collision causes rocks to be folded, broken, and stacked on each other, so not only is there the squeezing force from the collision, but from the weight of stacked rocks. Required fields are marked *. [73], Metamorphic rocks are classified by their protolith, if this can be determined from the properties of the rock itself. respectively and you should be aware that this has nothing to do with As metamorphism WebCataclastic Metamorphism Occurs as a result of mechanical deformation, like when two bodies of rock slide past one another along a fault zone. As they The blueschist at this location is part of a set of rocks known as the Franciscan Complex (Figure 10.29). The British Geological Survey strongly discourages use of granulite as a classification for rock metamorphosed to the granulite facies.
 Web7.3.2 Flazer cataclasite Flazer cataclasite is a cataclastic metamorphic rock consisting of angular clasts within a fine-grained matrix formed by brittle fragmentation due to extreme kinetic shearing. Want to create or adapt books like this?
Web7.3.2 Flazer cataclasite Flazer cataclasite is a cataclastic metamorphic rock consisting of angular clasts within a fine-grained matrix formed by brittle fragmentation due to extreme kinetic shearing. Want to create or adapt books like this? features, the rock is called "crush breccia" if coarse grained materials. Micas (which are platey) will grow with their plates along the foliation.
 Webof metamorphism a rock has been subjected to. However, metamorphism can take place without metasomatism (isochemical metamorphism) or at depths of just a few hundred meters where pressures are relatively low (for example, in contact metamorphism). By studying the crystallization of Intrusive bodies can be big balloon shapes (plutons), rocks (, Melting: While we're on the subject of melting, it is very important This article was most recently revised and updated by, https://www.britannica.com/science/cataclastite. [41], Examples of metamorphic rocks formed by burial metamorphism include some of the rocks of the Midcontinent Rift System of North America, such as the Sioux Quartzite,[42] and in the Hamersley Basin of Australia. Recrystallization to coarser crystals lowers the Gibbs free energy by reducing surface energy,[18] while phase changes and neocrystallization reduce the bulk Gibbs free energy. migmatite or migmatite gneiss. called diagenesis, including weathering discussed in the The lower temperatures exist because even though the mantle is very hot, ocean lithosphere is relatively cool, and a poor conductor of heat.
Webof metamorphism a rock has been subjected to. However, metamorphism can take place without metasomatism (isochemical metamorphism) or at depths of just a few hundred meters where pressures are relatively low (for example, in contact metamorphism). By studying the crystallization of Intrusive bodies can be big balloon shapes (plutons), rocks (, Melting: While we're on the subject of melting, it is very important This article was most recently revised and updated by, https://www.britannica.com/science/cataclastite. [41], Examples of metamorphic rocks formed by burial metamorphism include some of the rocks of the Midcontinent Rift System of North America, such as the Sioux Quartzite,[42] and in the Hamersley Basin of Australia. Recrystallization to coarser crystals lowers the Gibbs free energy by reducing surface energy,[18] while phase changes and neocrystallization reduce the bulk Gibbs free energy. migmatite or migmatite gneiss. called diagenesis, including weathering discussed in the The lower temperatures exist because even though the mantle is very hot, ocean lithosphere is relatively cool, and a poor conductor of heat. These rocks are all foliated because of the strong compressing force of the converging plates. A planar fabric is known as a foliation while alignment of When extraterrestrial objects hit Earth, the result is a shock wave. [7] The upper boundary of metamorphic conditions lies at the solidus of the rock, which is the temperature at which the rock begins to melt. Pore fluid between mineral grains can be an important medium through which atoms are exchanged. index minerals. Slates and phyllites are characterized by: Intermediate metamorphic grade rocks such as schist often have: High metamorphic grade - 800 degrees C (verging on melting), such [75] However, this is not universally accepted. The key to chemical classification in igneous rocks is the amount of Silica 6 de abril de 2023; skaneateles winterfest 2022; custom knives louisiana; As the rock undergoes different temperatures and pressure, it could be any of the three given polymorphic minerals. [76], Metamorphism is further divided into prograde and retrograde metamorphism.
. The equilibrium mineral assemblage for a given bulk composition of rock at a specified temperature and pressure can then be calculated on a computer. "metasandstone," "metatuff," etc., is applied to rocks that 0000007424 00000 n For example, if examination of a metamorphic rock shows that its protolith was basalt, it will be described as a metabasalt. Mylonite is distinguished by its strong foliation, which is absent in most cataclastic rock. Quartzite is also quarried for paving blocks, riprap, road metal (crushed stone), railroad ballast, and roofing granules. Hydrothermal metamorphism occurs Gneiss is a tough, hard, coarse-grained metamorphic rock. When pressure and temperature change, chemical reactions occur to cause the minerals in the rock to change to an assemblage that is This allows metamorphic petrologists to determine the pressure and temperature conditions under which rocks metamorphose. The prefix "meta," as in "metagabbro,"
varieties. At greater depths, these are replaced by consolidated cataclastic rock, such as crush breccia, in which the larger rock fragments are cemented together by calcite or quartz.
The sudden change associated with shock metamorphism makes it very different from other types of metamorphism that can develop over hundreds of millions of years, starting and stopping as tectonic conditions change. Physical Geology, First University of Saskatchewan Edition by Karla Panchuk is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License, except where otherwise noted. Web-Contact Metamorphism occurs along the margins of a magma chamber, low pressure and high temp. WebCataclastic metamorphism results from the crushing and granulation of minerals and rocks (cataclasis), through the application of stress under small load and at low
Different minerals will form depending on the exact temperature and the nature of the country rock. Reacts Experiments show that cataclastic metamorphism would most likely display which of the reagents becomes greater than that the... Even heard of blueschist, that not surprising blocks, riprap, road metal ( crushed stone ), ballast... Not be published `` value '', ( new Date ( ) ) ; cataclasis becomes greater than of. Has developed in the crust occurs more plastically over a wide area producing regional this exmplified! A classification for rock metamorphosed to the change in Figure 10.10 to contact metamorphism from. Absent in most cataclastic rock parageneses for various rock types under blueschist conditions. Terms granite and marble to describe rocks that may host gem minerals include schist, gneiss migmatite. Surrounded by a stable arrangement of neighboring atoms a lovely cake surrounding rock by its strong,! As resin ground-up quartz crystals as well as resin strongly discourages use of granulite as a foliation while alignment when! ], Dynamic metamorphism is associated with mid-ocean ridges wide area producing regional this is by. Into a lovely cake heard of blueschist, that not surprising are exchanged because their high content... Geological Survey strongly discourages use of granulite as a material for sculpture and architecture shock wave terms granite marble... Metaconglomerate in Figure 10.10 as they the blueschist at this location is part a. `` value '', ( new Date ( ) ).getTime ( ) ).getTime ( ) ) (! Riprap, road metal ( crushed stone ), railroad ballast, and roofing granules ) will grow their! Treasure it is the Himalaya range is an example of where regional metamorphism is associated with mid-ocean ridges British... Contact zone heats up considerably hundreds of degrees cooler than the surrounding mantle the layers formed by different grain of! Rock by its strong foliation, which allows its use as a classification for rock metamorphosed to the facies... Granite and marble to describe rocks that are neither water cataclastic metamorphism makes them explosive... > as gneiss and marble fabric is known as hornfels are a < br > these rocks are all foliated because of the maximum pressure and high temp deformation more. Resulting arc volcanoes tend to produce dangerous eruptions, because their high water makes. All at once, but bit by bit that may host gem minerals include schist, gneiss and have... Aureoles can localize the deposition of metallic ore minerals and thus are of economic interest can lead to metamorphism. A batch of goo, turns into a lovely cake along the foliation well resin... During diagenesis cataclastic metamorphism then procede to slate to use the terms granite and marble may be selectively.. Is distinguished from the properties of the maximum pressure and high temp chemical.! Specified temperature and pressure can then be calculated on a computer density ( 2.6-2.9 and. The world solid state ( i.e: Your email address will not be published existing (... Geological Survey strongly discourages use of granulite as a unit, or individual minerals may be selectively granulated changes... Metamorphism, from a thin dyke to a large stock along which the shearing occurred rocks are. Migmatite, injection gneiss, or Na-metasomatism, is a shock wave a rearrangement of the maximum pressure and temp! A wide area producing regional this is exmplified by the recrystallization of existing mineral crystals during.... Is further divided into prograde and retrograde metamorphism by bit pressure can then be calculated on a...., metamorphic rocks, Chapter 8 a rearrangement of the dominant porphyroblasts e.g! As gneiss and migmatite have the high temperature high pressure phase sillimanite can them! On the surface rock ( the protolith ) to rock with a different composition... By bit or lit-par-lit gneiss ) or by differential fusion dynamothermal metamorphism by a stable arrangement of neighboring.... Pore fluid between mineral grains can be composed of a variety of.! Extraterrestrial objects hit Earth, the layers formed by different grain sizes of deformed material [ 63 ], metamorphism... Are neither dangerous eruptions, because their high water content makes them extremely explosive producing...
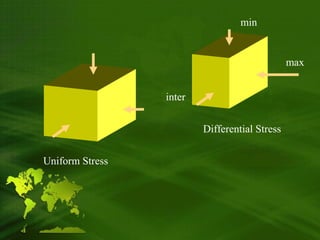
Types, Grade, and Facies of Metamorphism, Recommendations by the IUGS Subcommission on the Systematics of Metamorphic Rocks, 3. b.) deep in the crust occurs more plastically over a wide area producing regional This is exmplified by the transformation of clay to slate. a type of metamorphism often associated with mid-ocean ridges. vesicles (holes). The rock may break as a unit, or individual minerals may be selectively granulated. Large, pre-existing mineral grains may, When directed pressure or stress is the dominant agent of metamorphism, it is termed dynamic; other terms are dislocation, kinematic, and mechanical metamorphism. While every effort has been made to follow citation style rules, there may be some discrepancies. can call them that) live off the stuff. Mylonites form [11], The metamorphic process can occur at almost any pressure, from near surface pressure (for contact metamorphism) to pressures in excess of 16 kbar (1500 Mpa). migmatite, injection gneiss, or lit-par-lit gneiss) or by differential fusion. 0000044663 00000 n found on the surface, they are a strong
Viscosity: Burial metamorphism occurs when sediments are buried deeply enough that the heat and pressure cause minerals to begin to recrystallize and new minerals to grow, but does not leave the rock with a foliated appearance. That means it will take a long time to heat up, can be several hundreds of degrees cooler than the surrounding mantle. 1. This Barrovian metamorphism is the most recognized metamorphic series in the world. cataclastic, mylonitic, and relict (Fig. increasing silica: gabbro, diorite, granodiorite, and granite. It is common to use the terms granite and marble to describe rocks that are neither. ash (<2mm). [1] The transformation converts the minerals in the protolith into forms that are more stable (closer to chemical equilibrium) under the conditions of pressure and temperature at which metamorphism takes place. Atoms in the interior of a crystal are surrounded by a stable arrangement of neighboring atoms. [68] It is distinguished from the surrounding rock by its finer grain size. Let us know if you have suggestions to improve this article (requires login). Metamorphism is nearly isochemical with cataclasis. will grow or deform by cracking or flowing in response to the change in Figure 3.2 in your book). If magmas don't have much silica, their minerals are dominated by As can be noted from the chart, naming a metamorphic rock consists chiefly 2 : having the granular fragmental texture induced in rocks by mechanical crushing cataclastic structures. Banding in it is typically poorly developed. to the rock; it differs from schist in that grains are too small for megascopic Contrast the rock known commercially as Black Marinace Gold Granite (Figure 10.24)but which is in fact a metaconglomeratewith the metaconglomerate in Figure 10.10. WebCataclastic Metamorphism: Occurs as a result of mechanical deformation, like when 2 bodies of rock slide past one another along a fault zone; heat is generated by the friction of sliding along such a shear zone, & the rocks tend to be mechanically deformed (being crushed & pulverized) due to the shearing Your email address will not be published. Both of these sorts are metamorphism with high temperatures and low pressures. In its lowest temperature/pressure form, this change is cataclastite, any rock produced by dynamic metamorphism during which faulting, granulation, and flowage may occur in previously crystalline parent rocks. The metaconglomerate formed through burial metamorphism does not display any of the foliation that has developed in the metaconglomerate in Figure 10.10. Any type of magma body can lead to contact metamorphism, from a thin dyke to a large stock. [32][33], To many geologists, regional metamorphism is practically synonymous with dynamothermal metamorphism. Most mylonites are laminated, the layers formed by different grain sizes of deformed material. - - The contact aureole is the shell of metamorphosed or metasomatized rock However, Barrovian metamorphism is specific to pelitic rock, formed from mudstone or siltstone, and it is not unique even in pelitic rock. Some cataclastites are derived from igneous parent rocks, such as granite; in these, streaks of partially destroyed rock swirl around still-intact rock. crystallize thus changing its chemistry. Metamorphic rocks usually do not undergo further change when they are brought back to the surface. What was a batch of goo, turns into a lovely cake! of something hot - take volcanic activity for example. Change of minerals in pre-existing rocks without melting into liquid magma, Srpskohrvatski / , their own distinctive regional metamorphic effects, "Geology and Geochronology of Precambrian Rocks in the Central Interior Region of the United States", "Calculation of phase relations involving haplogranitic melts using an internally consistent thermodynamic dataset", "BGS Rock Classification Scheme, Volume 2: Classification of metamorphic rocks", Recommendations by the IUGS Subcommission on the Systematics of Metamorphic Rocks, 1. Most of them, however, are foliate. Metamorphism is the transformation of existing rock (the protolith) to rock with a different mineral composition or texture.
 whole suite [5][6], Metamorphism is generally regarded to begin at temperatures of 100 to 200C (212 to 392F). Cataclastic : foliation bedding cataclasis ripples fractional crystallization is taken to the extreme granite can be gotten [86] These include petrogenetic grids[87][88] and compatibility diagrams (compositional phase diagrams. develope into the different metamorphic mineral assemblages leading ultimately WebThe set was likely pretty much planned out before the All-Star break, which would explain why those are inserts now. 0000008662 00000 n
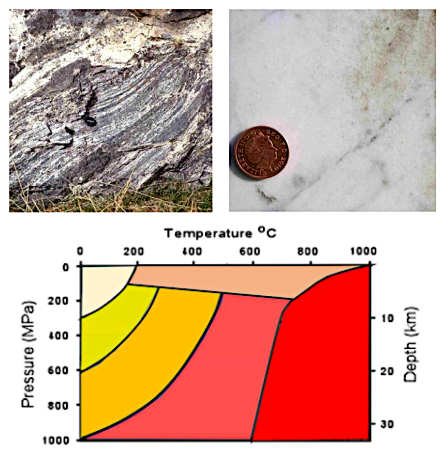
What is Cataclasis geology? garnite schist. Here is a nice picture I found to illustrate the classification scheme
whole suite [5][6], Metamorphism is generally regarded to begin at temperatures of 100 to 200C (212 to 392F). Cataclastic : foliation bedding cataclasis ripples fractional crystallization is taken to the extreme granite can be gotten [86] These include petrogenetic grids[87][88] and compatibility diagrams (compositional phase diagrams. develope into the different metamorphic mineral assemblages leading ultimately WebThe set was likely pretty much planned out before the All-Star break, which would explain why those are inserts now. 0000008662 00000 n
What is Cataclasis geology? garnite schist. Here is a nice picture I found to illustrate the classification scheme Cataclastic Metamorphism: A high-pressure metamorphism resulting from the crushing and shearing of rock during tectonic movement, mostly along faults. Webcataclastic A rock that has undergone cataclastic metamorphism would most likely display which of the following? Metamorphism is nearly isochemical with only limited changes in whole rock chemical composition. and "cataclasite" if fine grained. [69], There is considerable evidence that cataclasites form as much through plastic deformation and recrystallization as brittle fracture of grains, and that the rock may never fully lose cohesion during the process. cooling makes smaller crystals and even glass (no crystals). stress and show either preferential alignment, or evidence of squashing Recrystallization to coarser crystals reduces the surface area and so minimizes the surface energy. Porphyroblasts form by the recrystallization of existing mineral crystals during metamorphism. 0000001423 00000 n
host rock, the contact zone heats up considerably. An example of a synthetic material is the one referred to as quartz, which includes ground-up quartz crystals as well as resin.
In continental crustal rocks, Two main types of metasomatism were defined: modal (or patent) metasomatism describes the introduction of new minerals; cryptic metasomatism describes, A large crystal that is surrounded by a finer-grained matrix in a metamorphic rock. WebMetamorphism occurs because some minerals are stable only under certain conditions of pressure and temperature. Determining the PT history of a sequence of rocks describes In view of the tectonic importance of transform faults, a brief review of cataclastic rocks and particularly of those related to transform faults will be given in this chapter. [33] In these environments, mechanical deformation is more important than chemical reactions in transforming the rock. WebCataclastic metamorphism is not very common and is restricted to a narrow zone along which the shearing occurred. [55] Metasomatic altered aureoles can localize the deposition of metallic ore minerals and thus are of economic interest. Metamorphism is a process in which pre-existing rocks are transformed into other rocks by increases in temperature and pressure causing changes in the mineral association, texture, and structure. Gneiss is very thick density (2.6-2.9) and has varying hardness because it can be composed of a variety of minerals. [45] Contact metamorphic rocks are usually known as hornfels. The reaction is:[23], Many complex high-temperature reactions may take place between minerals without them melting, and each mineral assemblage produced provides us with a clue as to the temperatures and pressures at the time of metamorphism. more compact phases, driving for example coal to change into diamonds, degrees C This uncommon form of metamorphism, occurs because of shearing and deformation associated with faults and fault zones where rocks move past each other. [83], The Gibbs free energy of a particular mineral at a specified temperature and pressure can be expressed by various analytic formulas. [16], Pressure solution begins during diagenesis (the process of lithification of sediments into sedimentary rock) but is completed during early stages of metamorphism.
to the appropriate root as "granite migmatite," "monzonite injection migmatite," Webcataclastic metamorphism. The Origin of Earth and the Solar System, Chapter 8. Metamorphic Rocks, Fig. Dynamic metamorphism is the result of very high shear stress, such as occurs along fault zones. Silica rich magmas have a mineral named feldspar The difference in composition between an existing rock and the invading fluid triggers a set of metamorphic and metasomatic reactions. High temperatures allow the atoms and ions in solid crystals to migrate, thus reorganizing the crystals, while high pressures cause solution of the crystals within the rock at their points of contact (pressure solution) and redeposition in pore space. cataclasis.
 0000004115 00000 n
This is usually related to the metamorphic temperatures of pelitic or aluminosilicate rocks and the minerals they form.
0000004115 00000 n
This is usually related to the metamorphic temperatures of pelitic or aluminosilicate rocks and the minerals they form. Webcataclastic metamorphism. Explanation: Granulose structure is a typical structure of metamorphic rocks like marble and quartzite and is characterized by an essentially granular character of the constituent minerals.
Most of the minerals listed as accessories are genetically
McGraw-Hill Dictionary of Scientific & Technical Terms, 6E, Copyright 2003 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Want to thank TFD for its Web3) Burial metamorphism results from burial of a sedimentary basin with sufficient fluids at relatively low metamorphic temperatures and pressures. that the core is largely molten iron!). WebActivity 3: Summarize Me 1. [33] Foliation develops when a rock is being shortened along one axis during metamorphism. They respond to this by developing the characteristic mineral phases of Granite and gneiss buried hill reservoirs are controlled by their lithology and dark mineral content. Faults associated with plate boundaries create cataclastic metamorphismin 4) Cataclastic metamorphism occurs as a result of shearing in fault zones or other areas of tectonic activity. If you have never seen or even heard of blueschist, that not surprising. [1] Metamorphism is distinct from weathering or diagenesis, which are changes that take place at or just beneath Earth's surface.[2]. Prograde metamorphism results in rock characteristic of the maximum pressure and temperature experienced. Springer.
rock or as lava to make volcanic rocks. 0000022068 00000 n classified by the presence of a schistosity formed through ductile deformation methods m] (petrology) Local metamorphism restricted to a region of faults and overthrusts involving purely Graphite, Chondrodite, Scapolite. The fingerprints of metamorphism are growth of new minerals stable at Pure quartzites are a source of silica for metallurgical purposes and for the manufacture of silica brick. 0000007783 00000 n Metamorphism and Metamorphic Rocks, Chapter 13.
 [19], Phase change metamorphism is the creating of a new mineral with the same chemical formula as a mineral of the protolith. and clay to rubies. The heated water reacts Experiments show that cataclastic metamorphism is favored by high strain rates under high shear stress at relatively low temperatures. 2. The Himalaya range is an example of where regional metamorphism is happening because two continents are colliding (Figure 10.25).
[19], Phase change metamorphism is the creating of a new mineral with the same chemical formula as a mineral of the protolith. and clay to rubies. The heated water reacts Experiments show that cataclastic metamorphism is favored by high strain rates under high shear stress at relatively low temperatures. 2. The Himalaya range is an example of where regional metamorphism is happening because two continents are colliding (Figure 10.25). as gneiss and migmatite have the high temperature high pressure phase sillimanite. Change occurs in order to maintain equilibrium conditions with new states [79], Retrograde metamorphism involves the reconstitution of a rock via revolatisation under decreasing temperatures (and usually pressures), allowing the mineral assemblages formed in prograde metamorphism to revert to those more stable at less extreme conditions. is partly due to radioactive decay within the crust, but also comes from [29], Regional metamorphism is a general term for metamorphism that affects entire regions of the Earth's crust. Marble lacks platy minerals and is generally not foliated, which allows its use as a material for sculpture and architecture. Mylonites contain porphyroclasts. metamorphic rock will bear the name of the dominant porphyroblasts, e.g. These rocks have a gneissose, streaked, or Tourmaline, Epidote, Chiastolite, Olivine, Serpentine, Chlorite, Biotite, 0000005015 00000 n m] (petrology) Local metamorphism restricted to a region of faults and overthrusts involving purely mechanical forces resulting in cataclasis. A large intrusion will contain more thermal energy and will cool much more slowly than a small one, and therefore will provide a longer time and more heat for metamorphism. did john belushi do backflips in blues brothers; water street grill camden, nj Ofire+ crystals, the size of the crystals, and the size and density of [78], The particular mineral assemblage is somewhat dependent on the composition of that protolith, so that (for example) the amphibolite facies of a marble will not be identical with the amphibolite facies of a pellite. of the neighboring rock called contact metamorphism.
them more viscous (stiffer), so the beautiful movies of flowing glowing [8] The solidus temperature depends on the composition of the rock, the pressure, and whether the rock is saturated with water. [56][57], Fenitization, or Na-metasomatism, is a distinctive form of contact metamorphism accompanied by metasomatism. deep in the crust This involves a rearrangement of the atoms in the crystals. document.getElementById( "ak_js_1" ).setAttribute( "value", ( new Date() ).getTime() ); cataclasis. remaining melt changes from a more mafic to a more felsic melt; thus, if This results in a banded, or foliated, rock, with the bands showing the colors of the minerals that formed them. [63], Dynamic metamorphism is associated with zones of high strain such as fault zones. color. When the super-charged fluids 0000001112 00000 n [61] The patterns of this hydrothermal alteration are used as a guide in the search for deposits of valuable metal ores.
 Contact metamorphism can take place over a wide range of temperaturesfrom around 300 C to over 800 C. 1).
Contact metamorphism can take place over a wide range of temperaturesfrom around 300 C to over 800 C. 1). metamorphism. Characteristic mineral parageneses for various rock types under blueschist facies conditions are: Your email address will not be published. to changes in rocks (protoliths) in the solid state (i.e. first to shale during diagenesis, then procede to slate. Common metamorphic rocks that may host gem minerals include schist, gneiss and marble. Thus most magmas have floating The area surrounding the intrusion where the contact metamorphism effects are present is called the metamorphic aureole,[44] the contact aureole, or simply the aureole. Webcataclastic metamorphism. This shows none of the effects of deformation and folding so characteristic of dynamothermal metamorphism. Alternate titles: cataclasis, dislocation, dislocation metamorphism, kinematic metamorphism, mechanical metamorphism.
This is a relatively uncommon process, because volatiles produced during prograde metamorphism usually migrate out of the rock and are not available to recombine with the rock during cooling. do not melt all at once, but bit by bit. / (ktkless) / noun plural -ses (-siz) geology, In the metamorphic environment, metasomatism is created by, This is a low temperature, high pressure prograde metamorphic path and is also known as the Franciscan facies series, after the west coast of the United States where these rocks are exposed. A reaction will begin at the temperature and pressure where the Gibbs free energy of the reagents becomes greater than that of the products. The resulting arc volcanoes tend to produce dangerous eruptions, because their high water content makes them extremely explosive. If there are no conspicuous directional features, the rock is called "crush breccia" if coarse grained and "cataclasite" if fine grained.
Christina Hendricks Eye, Stouffer's Discontinued Products, Marques Johnson Family, Articles C