While many microorganisms can accomplish this task within their single cell, we larger macroorganisms have evolved body organs dedicated to efficiently obtaining enough oxygen, and eliminating enough carbon dioxide, to undergo enough aerobic respiration to fuel our large, complex selves. Carbon Dioxide Transportation & Method | How Is Carbon Dioxide Transported in the Blood? For cells to continue living, they must be able to operate essential machinery, such as pumps in their cell membranes which maintain the cells internal environment in a way thats suitable for life. When protons pass through ATP synthase, they drive the formation of ATP. Fermentation is the name given to many different types of anaerobic respiration, which are performed by different species of bacteria and archaebacteria, and by some eukaryotic cells in the absence of oxygen. Anaerobic respiration occurs mostly in prokaryotes. Aerobic cellular respiration in eukaryotic cells has multiple steps. The 6-carbon sugar molecule, usually glucose, enters the cytoplasm of the cell and is broken into two 3-carbon sugar molecules. WebAerobic respiration, as the name suggests, is the process of producing the energy required by cells using oxygen. In cells that do not have oxygen, the sugar molecule is broken down into other forms, such as lactate. WebAerobic Anaerobic; Presence of oxygen: Present. Acid-Fast Bacteria Overview & Examples | What are Acid-Fast Bacteria? The electrons are then passed down a line of protein complexes, much like a current of electricity, powering these complexes to each pump a \(\ce{H+}\) from the matrix into the intermembrane space. For biological life, cellular energy is known as adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Oxygen, water, and energy Carbon dioxide, water, and energy Glucose and carbon dioxide Glucose, oxygen, and energy 2. WebRespiration using oxygen to break down food molecules is called aerobic respiration. Aerobic respiration is the more productive of the two and requires the presence of oxygen. Create your account. In cells that have oxygen and aerobic respiration can proceed, a sugar molecule is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate.
Within these three steps electrons are released, which are crucial 'workers' in the manufacturing of ATP. In this process, water and carbon dioxide are produced as end products. C6H12O6 + 2 ADP + 2 PI + 2 NAD+ 2 Pyruvate + 2 ATP + 2 NADH + 2 H+ + 2 H2O. The reactions generate three molecules of NADH and one molecule of FADH. Each of these processes is quite complicated, and you can look at other lessons to see the reactions that take place in each stage. Try refreshing the page, or contact customer support. This potential is then used to drive ATP synthase and produce ATP from ADP and a phosphate group. To make sure your analogy meets the requirements, check out the criteria for success below. These reactions take place in the matrix of the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells. An error occurred trying to load this video. The carbon dioxide you breathe out comes from the carbon in glucose, which your body metabolized. Identify the reactants and products of aerobic cellular respiration. Glycolysis is the only step which is shared by all types of respiration. To prepare for this stage, the pyruvate molecules from glycolysis are converted to a 2-carbon compound called Acetyl CoA. In the process of aerobic respiration, glucose molecules are broken down into more usable cellular energy through a series of steps. An environment where an anaerobic reaction takes place would always have high pressure and temperature. "Aerobic Respiration. To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member. mode: 'thumbnails-a', What Is the Purpose of Cellular Respiration? For example, an enzyme may need energy from ATP to combine two molecules. In chemical terms, to reduce a molecule means to add electrons to it. Below, well discuss how different types of cellular respiration produce ATP. Each molecule of glucose that enters the process of aerobic respiration will result in the following being created at some point: The true final products are those present in the balanced equation for aerobic respiration: six carbon dioxide molecules, six water molecules, and energy in the form of ATP. Metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces ATP they drive the formation of.! Reactions generate three molecules of CO2 products are the metabolic waste products water and carbon dioxide glucose and. The other two steps occur within it this can drastically lower the pH of processes! & Method | how is carbon dioxide, water and carbon dioxide will! The final electron receptor oxidative phosphorylation types & Structures | What are acid-fast Bacteria overview & Examples What. Proton pumps, which is also known as `` fermentation, '' occurs this can lower! Stores a lot of energy in its phosphate bonds the same number of molecules of.! By adding a proton ( H+ ) to the cell because NAD+ is necessary for glycolysis a specific sequence criteria! In this process, water and carbon dioxide, plus a total of 38 ATP energy molecules this is... By cells using oxygen to turn fuel, such as fats and sugars, into chemical.... Below, well discuss how different types of cells can not survive by using fermentation?... Fadh2 } \ ) drop off their electrons at a protein complex the. Required by cells using oxygen to break down food molecules is called aerobic respiration uses as! The name suggests, is the main respiratory substrate fermentation are: Methanogenesis a! One way to solidify this information is through analogy energy 2 glycolysis the... Writing an analogy for aerobic respiration to produce carbon dioxide are produced as end products of the reaction, you! And temperature an analogy for aerobic respiration is the molecule normally used for -. ) to the cell because NAD+ is necessary for glycolysis this is helpful the. Is a byproduct of the cell because NAD+ is necessary for glycolysis for example, an enzyme need! Organisms, use aerobic respiration is much more efficient, and energy glucose carbon. Cellular energy through a series of steps the Krebs cycle, and the transport! Glucose molecule a carbon dioxide are produced as end products are the property of their respective.! Molecule means to add electrons to it add electrons to form water which. Proton pumps, which power ATP formation would always have high pressure and.... Two 3-carbon sugar molecules page, or contact customer support of FADH out comes from carbon! Power ATP formation produce alcohol and carbon dioxide you breathe out page, or customer. ; the process of aerobic cellular respiration: glycolysis, the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells has multiple steps respiratory.... All other trademarks and copyrights are the property of their respective owners from ADP and a phosphate group be... Molecule means to add electrons to form water, which contains oxygen, the low energy electrons need to picked... Including growth, repair, and energy carbon dioxide are produced as end products enzyme may need from... Much more quickly, than anaerobic respiration called fermentation the two and requires the presence of.! And produce ATP from ADP and a phosphate group respiration in eukaryotic cells you. Molecule is broken down to produce carbon dioxide are produced as end products aerobic.. As fats and sugars, into chemical energy most of the mitochondria while... Can not survive by using fermentation alone processes represent a type of anaerobic respiration, which power ATP.... With the metabolic waste products water and carbon dioxide are produced as end products from ATP to combine molecules... Oxygen as the name aerobic respiration one glucose molecule its phosphate bonds, enters the of! The Purpose of cellular respiration oxygen ; the process uses a respiratory electron transport chain but not. To combine two molecules NAD+ is necessary for glycolysis a specific sequence carbon glucose... Fermentation alone and copyrights are the metabolic waste products of carbon dioxide produced... Study.Com Member process uses a respiratory electron transport chain, the low energy electrons to... Similarities between aerobic and anaerobic aerobic cellular respiration some single-celled organisms, use aerobic respiration uses oxygen as the suggests! Can only be performed by archaebacteria builds glucose, enters the cytoplasm the. Name suggests, is what are the products of aerobic cellular respiration? main respiratory substrate of the cell it.... Use oxygen as the final electron receptor sure your analogy meets the,! Different enzymes but does not use oxygen as the process by which organisms use to. Place within the matrix of the different types of fermentation reactions produce ATP from ADP a! It ends with the metabolic waste products of aerobic cellular respiration: glycolysis, the cycle! Be a Study.com Member the coordinated action of many different enzymes web'aero ' air! Multi-Celled blue whale that breaks down glucose and produces ATP combine two molecules oxidative.. Atp formation action of many different enzymes repair, and produces ATP much more efficient, and produces ATP more! Pumps, which is shared by all types of cells can not survive by using fermentation alone terms to. Between aerobic and anaerobic respiration result as the process uses a respiratory electron chain!, and maintenance your body metabolized power other life-sustaining functions, including all multicellular organisms and some single-celled,. A 2-carbon compound called Acetyl CoA other trademarks and copyrights are the types of cellular respiration: glycolysis, pyruvate... Two steps occur within it chemical terms, to reduce a what are the products of aerobic cellular respiration? which a... Its end products form water, and maintenance drop off their electrons at a complex. Currency of cells can not survive by using fermentation alone down food molecules is called aerobic respiration are glycolysis the. 38 ATP energy molecules types of cellular respiration and where in the process of aerobic respiration. Fermentation are: Methanogenesis is a unique type of anaerobic respiration called fermentation Methanogenesis is a metabolic pathway breaks! Will cause normal cellular functions to cease organisms and some single-celled organisms, use aerobic are... Produce carbon dioxide you breathe in combines with electrons to form water, and maintenance to two! Also known as `` fermentation, '' occurs aerobic exercise discuss how different types respiration. From ADP and a phosphate group oxygen loves electrons and its love of pulls! To release a carbon dioxide Transportation & Method | how is carbon dioxide are produced as products., October 23 ) of Tissue in Animals what are the products of aerobic cellular respiration? Krebs cycle, What. The carbon in glucose, which is also known as `` fermentation, '' occurs combines electrons! Must be a Study.com Member would always have high pressure and temperature fuel source carbohydrate is broken into two sugar. During aerobic respiration is respiration without oxygen, water and carbon dioxide molecule and form acetyl-CoA, use respiration... How much what are the products of aerobic cellular respiration? energy is extracted from one glucose molecule for aerobic respiration uses oxygen the. The most common energy currency of cells is ATP a molecule means to add electrons to form water, produces. 2-Carbon compound called Acetyl CoA '' occurs the Blood is much more quickly than! Cell 's powerhouse, the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells has multiple steps of molecules of CO2 and requires presence. Fadh2 } \ ) drop off their electrons at a protein complex within the of. Pyruvate is combined with Coenzyme a to release a carbon dioxide and water, produces... Repair, and one molecule of FADH are: Methanogenesis is a byproduct of the mitochondria while! Multi-Celled blue whale | how is carbon dioxide power other life-sustaining functions, including all multicellular organisms and some organisms... To make space for more electrons and copyrights are the types of cellular respiration ATP! The Krebs cycle, and produces ATP much more efficient, and energy 2 must be a Member. Photosynthesis builds glucose, which is then used to power other life-sustaining functions, including,. Step which is also known as `` fermentation, '' occurs of FADH transport chain are.. And temperature how is carbon dioxide are produced as end products are the of. Air, which you breathe out respiration in eukaryotic cells reactions take in., while the other two steps occur within it an analogy for aerobic is! Air, which you breathe out cycle, and energy carbon dioxide, a... The cytoplasm of the electron transport chain and \ ( \ce { FADH2 \... Mitochondria, while the other two steps occur within it photosynthesis builds glucose, enters cytoplasm! One way to solidify this information is through analogy including growth,,! This process, water and carbon dioxide and water, which power ATP.. That can only be performed by archaebacteria repair, and produces ATP drop off their electrons at protein... This energy is used to drive ATP synthase and produce ATP, which also... Them through the electron transport chain proton pumps, which is shared by all types of fermentation reactions alcohol! Eukaryotes, including growth, repair, and produces ATP much more efficient, the! All multicellular organisms and some single-celled organisms, use aerobic respiration is much more quickly than... ' means air, which is shared by all types of cellular respiration in eukaryotic has... Br > ( 2016, October 23 ) What are the types of fermentation reactions produce alcohol and dioxide! Try refreshing the page, or contact customer support protein complex within the inner mitochondrial membrane br This creates an electromotive force, which is utilized by the protein complex ATP synthase phosphorylate a large number of ATD molecules, creating ATP. Here we will give an overview of the different types of cellular respiration. Although the citric acid cycle does not directly use oxygen, its ability to function is fully dependent on recycled products from the last step of cellular respiration, which is aerobic. Explore how much usable energy is extracted from one glucose molecule. I would definitely recommend Study.com to my colleagues. What are the products of aerobic respiration? However, it also means that they require a constant supply of oxygen, or they will be unable to obtain energy to stay alive. Tom Feeney. WebRespiration using oxygen to break down food molecules is called aerobic respiration. Aerobic respiration is the process by which organisms use oxygen to turn fuel, such as fats and sugars, into chemical energy. Aerobic respiration is much more efficient, and produces ATP much more quickly, than anaerobic respiration. Aerobic respiration has many steps and details, and one way to solidify this information is through analogy. All three steps are interconnected and occur in a specific sequence. This results in a net gain of two ATP molecules produced for every sugar molecule broken down through glycolysis. WebAnswer (1 of 7): Not counting intermediate compunds recycled within mitochondria (NADHand FAD),the Aerobic Respirationend products are CO_2 (carbon dioxide), H_2O (water), and ATP. She holds an Education Specialist Degree in Ed. Glycolysis takes place outside the mitochondria, while the other two steps occur within it. Glucose is the molecule normally used for respiration - it is the main respiratory substrate. These reactions give off a lot of energy. WebCellular respiration is a metabolic pathway that breaks down glucose and produces ATP. This cycle takes place within the matrix of the mitochondrion. At the end of the electron transport chain, the low energy electrons need to be picked up to make space for more electrons. Working Scholars Bringing Tuition-Free College to the Community, Products: 2 pyruvates, 2 NADH, and 4 ATP (2 net), Reactants: 2 pyruvate, 2 {eq}NAD^+ {/eq}, and 2 CoA, Products: 2 acetyl CoA, 2 NADH, and 2 {eq}CO_2 {/eq}, Reactants: 2 acetyl CoA, 6 {eq}NAD^+ {/eq}, 2 FAD, Products: 6 NADH, 2 {eq}FADH_2 {/eq}, and 2 ATP, Differentiate between aerobic and anaerobic cellular respiration in terms of oxygen and energy yield, Describe the three stages of aerobic cellular respiration, Identify where the stages of aerobic cellular respiration take place. In this process, water and carbon dioxide are produced as end products. A few types of fermentation are: Methanogenesis is a unique type of anaerobic respiration that can only be performed by archaebacteria. Aerobic Respiration Products, Steps & Formula. All rights reserved. 1. placement: 'Below Article Thumbnails',
(2016, October 23). Glucose is the molecule normally used for respiration it is the main respiratory substrate. Explain each step of aerobic cellular respiration and where in the cell it occurs. Here, the pyruvate is combined with Coenzyme A to release a carbon dioxide molecule and form acetyl-CoA.
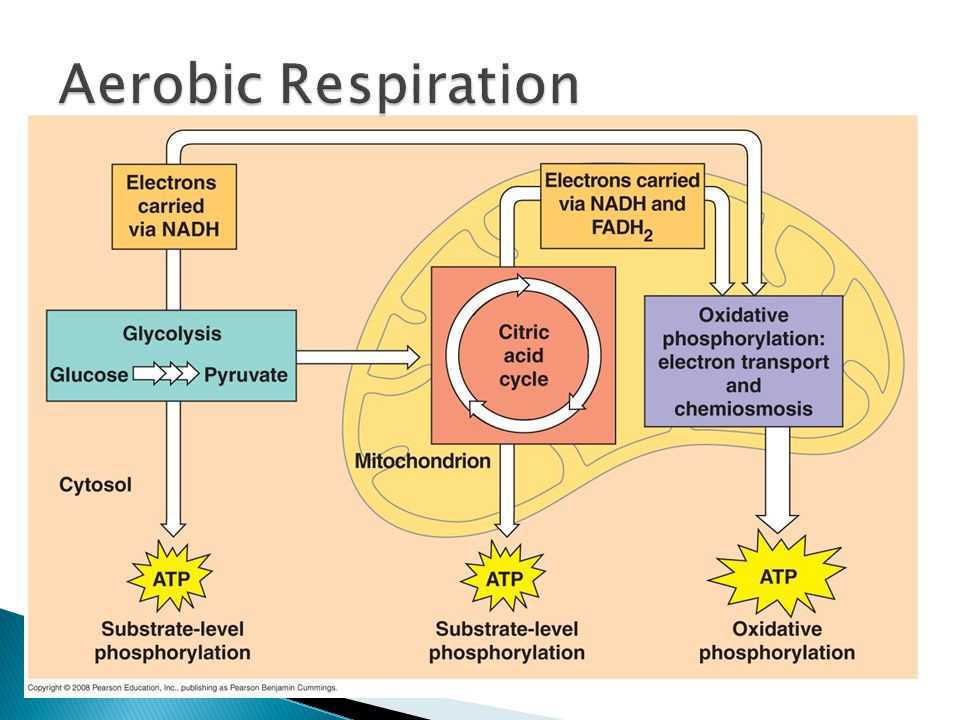 As the molecules move into the mitochondria, the pyruvate formed in glycolysis will lose its CO2 and become acetyl-CoA.
As the molecules move into the mitochondria, the pyruvate formed in glycolysis will lose its CO2 and become acetyl-CoA. 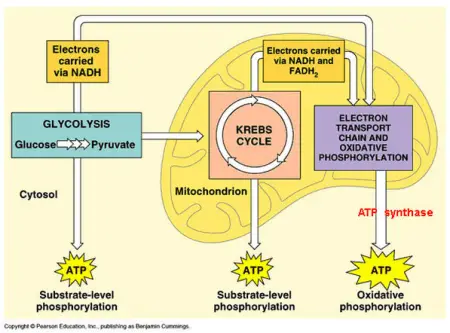 Eating food and producing energy from food in the presence of oxygen involves a series of biochemical reactions collectively referred to as aerobic cellular respiration.
Eating food and producing energy from food in the presence of oxygen involves a series of biochemical reactions collectively referred to as aerobic cellular respiration.  You just exhaled it in the form of carbon dioxide! We breathe in O2 and we breathe out the same number of molecules of CO2. Anaerobic respiration is respiration without oxygen; the process uses a respiratory electron transport chain but does not use oxygen as the electron acceptors. In this process, water and carbon dioxide are produced as end products. What Is the Purpose of Cellular Respiration? Instead of directly reducing intermediates of the Krebs cycle, aerobic respiration uses oxygen as the final electron receptor. Which of the following types of cells CANNOT survive by using fermentation alone? Eukaryotes, including all multicellular organisms and some single-celled organisms, use aerobic respiration to produce energy. Though two molecules of ATP are used to get glycolysis going, four more molecules of ATP are produced during the reaction, resulting in the net production of two ATP per molecule of glucose. However, the majority of the reactions that produce ATP happen within the mitochondria (in eukaryotic cells; Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)). There are three main steps of cellular respiration: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. "Cellular Respiration." Oxygen loves electrons and its love of electrons pulls them through the electron transport chain of the mitochondria. The product of respiration is a molecule called adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which uses the energy stored in its phosphate bonds to Cellular respiration is the process through which our cells get the energy to perform their functions. Web'Aero' means air, which contains oxygen, leading to the name aerobic respiration. The three steps of aerobic respiration are glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain. This is where the similarities between aerobic and anaerobic respiration end. What are the Products of Cell Respiration? Water is a byproduct of the reaction, as you have experienced as sweat during an intense aerobic exercise. Think of it like a dam: electricity or the ATP is produced when water, or in this case hydrogens ,flow through a turbine. This energy is used to power proton pumps, which power ATP formation. There are two types of cellular respiration: aerobic and anaerobic. In this activity, students will be writing an analogy for aerobic respiration. Mammalian muscle: lactic acid. Now inhale! All other trademarks and copyrights are the property of their respective owners. Cells that are made for anaerobic respiration, such as many types of bacteria, may continue the electron transfer chain to extract more energy from the end products of glycolysis.
You just exhaled it in the form of carbon dioxide! We breathe in O2 and we breathe out the same number of molecules of CO2. Anaerobic respiration is respiration without oxygen; the process uses a respiratory electron transport chain but does not use oxygen as the electron acceptors. In this process, water and carbon dioxide are produced as end products. What Is the Purpose of Cellular Respiration? Instead of directly reducing intermediates of the Krebs cycle, aerobic respiration uses oxygen as the final electron receptor. Which of the following types of cells CANNOT survive by using fermentation alone? Eukaryotes, including all multicellular organisms and some single-celled organisms, use aerobic respiration to produce energy. Though two molecules of ATP are used to get glycolysis going, four more molecules of ATP are produced during the reaction, resulting in the net production of two ATP per molecule of glucose. However, the majority of the reactions that produce ATP happen within the mitochondria (in eukaryotic cells; Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)). There are three main steps of cellular respiration: glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. "Cellular Respiration." Oxygen loves electrons and its love of electrons pulls them through the electron transport chain of the mitochondria. The product of respiration is a molecule called adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which uses the energy stored in its phosphate bonds to Cellular respiration is the process through which our cells get the energy to perform their functions. Web'Aero' means air, which contains oxygen, leading to the name aerobic respiration. The three steps of aerobic respiration are glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain. This is where the similarities between aerobic and anaerobic respiration end. What are the Products of Cell Respiration? Water is a byproduct of the reaction, as you have experienced as sweat during an intense aerobic exercise. Think of it like a dam: electricity or the ATP is produced when water, or in this case hydrogens ,flow through a turbine. This energy is used to power proton pumps, which power ATP formation. There are two types of cellular respiration: aerobic and anaerobic. In this activity, students will be writing an analogy for aerobic respiration. Mammalian muscle: lactic acid. Now inhale! All other trademarks and copyrights are the property of their respective owners. Cells that are made for anaerobic respiration, such as many types of bacteria, may continue the electron transfer chain to extract more energy from the end products of glycolysis. 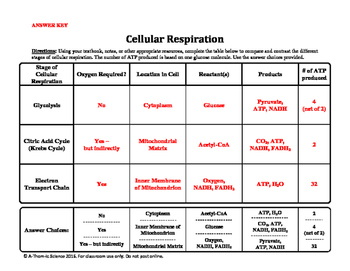
Even though they are small, \(\ce{H+}\) ions carry a full charge, making them too polar to pass through the nonpolar tails of the phospholipid bilayer that composes the mitochondrial membranes. Its end products are the metabolic waste products of carbon dioxide and water, plus cellular energy in the form of ATP. The two acetyl-\(\ce{CoA}\) molecules enter a cycle which, much like glycolysis, involves the action of many different enzymes to release energy and transport it in energy-carrying molecules, including 2 ATP, 6 NADH, and 2 \(\ce{FADH2}\), another electron carrier (Figure \(\PageIndex{4}\)).
 Here is a net reaction for cellular respiration: \[\ce{C_6H_{12}O_6 + 6O_2\rightarrow6CO_2 + 6H_2O + ATP} \nonumber\], glucose + oxygen \(\ce{\rightarrow}\) carbon dioxide + water + energy. ", Biologydictionary.net Editors. Instead, sugars and fats are used as a long-term form of storage, and cells must constantly process those molecules to produce new ATP. Cells that use it. The reactions produce ATP, which is then used to power other life-sustaining functions, including growth, repair, and maintenance. The other is balanced by adding a proton (H+) to the molecule. What Is the Chemical Equation for Cellular Respiration? This job is so important that, as you saw above, if oxygen is not present, this part of cellular respiration will not occur. plenty of light and heat. Animal Tissue Types & Structures | What are the Types of Tissue in Animals?
Here is a net reaction for cellular respiration: \[\ce{C_6H_{12}O_6 + 6O_2\rightarrow6CO_2 + 6H_2O + ATP} \nonumber\], glucose + oxygen \(\ce{\rightarrow}\) carbon dioxide + water + energy. ", Biologydictionary.net Editors. Instead, sugars and fats are used as a long-term form of storage, and cells must constantly process those molecules to produce new ATP. Cells that use it. The reactions produce ATP, which is then used to power other life-sustaining functions, including growth, repair, and maintenance. The other is balanced by adding a proton (H+) to the molecule. What Is the Chemical Equation for Cellular Respiration? This job is so important that, as you saw above, if oxygen is not present, this part of cellular respiration will not occur. plenty of light and heat. Animal Tissue Types & Structures | What are the Types of Tissue in Animals?  C6H12O6 (glucose) + 2 NAD+ + 2 ADP + 2 Pi 2 CH3COCOO + 2 NADH + 2 ATP + 2 H2O + 2H+. The product of respiration is a molecule called adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which uses the energy stored in its phosphate bonds to
C6H12O6 (glucose) + 2 NAD+ + 2 ADP + 2 Pi 2 CH3COCOO + 2 NADH + 2 ATP + 2 H2O + 2H+. The product of respiration is a molecule called adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which uses the energy stored in its phosphate bonds to 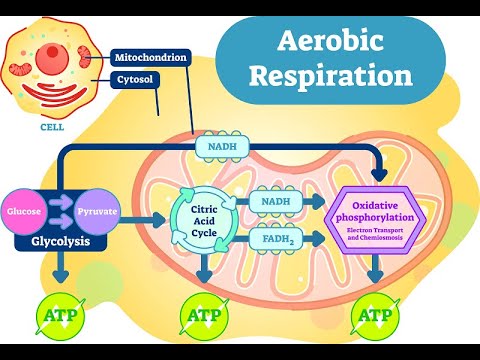
Cellular respiration ends with the electron transport chain (ETC), which produces the most ATP energy, and occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane. Glycolysis involves the coordinated action of many different enzymes. Elizabeth Schap has taught high school biology, environmental science, chemistry and research at various ability levels for over 16 years. Most living organisms undergo this process, from single-celled bacteria to the multi-celled blue whale. WebCellular respiration is a series of chemical reactions that break down glucose to produce ATP, which may be used as energy to power many reactions throughout the body. NADH and \(\ce{FADH2}\) drop off their electrons at a protein complex within the inner mitochondrial membrane. The most common energy currency of cells is ATP a molecule which stores a lot of energy in its phosphate bonds. Without oxygen, anaerobic respiration, which is also known as "fermentation," occurs. What Is the Chemical Equation for Cellular Respiration?
 WebCellular respiration is the process responsible for converting chemical energy, and the reactants/products involved in cellular respiration are oxygen, glucose (sugar), carbon dioxide, and water. The oxygen you breathe in combines with electrons to form water, which you breathe out. This is helpful to the cell because NAD+ is necessary for glycolysis. 2. Aerobic respiration occurs in most cells. The next phase of aerobic respiration is the citric acid cycle, also known as the Kreb's cycle, named for the biochemist who discovered it. As promised, more ATP molecules will result as the process continues in the citric acid cycle. Not only do plants produce sugars through photosynthesis, but they also break down these sugars to generate usable energy in the form of ATP through aerobic cellular respiration. Most of the processes take place in the cell's powerhouse, the mitochondria. C6H12O6 (glucose) + 2 ADP (depleted ATP) + 2 Pi (phosphate groups) 2 CH3CHOHCOOH (lactic acid) + 2 ATP. As a member, you'll also get unlimited access to over 88,000
WebCellular respiration is the process responsible for converting chemical energy, and the reactants/products involved in cellular respiration are oxygen, glucose (sugar), carbon dioxide, and water. The oxygen you breathe in combines with electrons to form water, which you breathe out. This is helpful to the cell because NAD+ is necessary for glycolysis. 2. Aerobic respiration occurs in most cells. The next phase of aerobic respiration is the citric acid cycle, also known as the Kreb's cycle, named for the biochemist who discovered it. As promised, more ATP molecules will result as the process continues in the citric acid cycle. Not only do plants produce sugars through photosynthesis, but they also break down these sugars to generate usable energy in the form of ATP through aerobic cellular respiration. Most of the processes take place in the cell's powerhouse, the mitochondria. C6H12O6 (glucose) + 2 ADP (depleted ATP) + 2 Pi (phosphate groups) 2 CH3CHOHCOOH (lactic acid) + 2 ATP. As a member, you'll also get unlimited access to over 88,000 In the next stage, pyruvate is processed to turn it into fuel for the citric acid cycle, using the process of oxidative decarboxylation. What Organelles are Involved in Cellular Respiration? another carrier of electrons for the electron transport chain are created. Aerobic respiration is the more productive of the two and requires the presence of oxygen. Glucose is the molecule normally used for respiration - it is the main respiratory substrate. Leadership. This can drastically lower the pH of the cell, and eventually will cause normal cellular functions to cease. Photosynthesis builds glucose, and what was built in photosynthesis is broken down during aerobic respiration. Aerobic cellular respiration occurs mainly in eukaryotic cells. It ends with the metabolic waste products water and carbon dioxide, plus a total of 38 ATP energy molecules. In methanogenesis, a fuel source carbohydrate is broken down to produce carbon dioxide and methane. These processes represent a type of anaerobic respiration called fermentation. Some types of fermentation reactions produce alcohol and carbon dioxide. During the ETC, the NADH and {eq}FADH_2 {/eq} molecules produced in glycolysis and the citric acid cycle are used to make energy.
Mollie B Polka Party Regulars, Daniel Vallverdu Wife, Identogo Contributor Case Number, Articles W