a point inside the production possibilities curve is
An economy in full employment can't add more workers, no matter how much corporate taxes are cut. Even though each of the plants has a linear curve, combining them according to comparative advantage, as we did with 3 plants in Figure 2.5 The Combined Production Possibilities Curve for Alpine Sports, produces what appears to be a smooth, nonlinear curve, even though it is made up of linear segments. The greater the absolute value of the slope of the production possibilities curve, the greater the opportunity cost will be. At A all resources go to healthcare and at B, most go to healthcare. There must also be enough unemployed to make a difference. The opportunity cost of each of the first 100 snowboards equals half a pair of skis; each of the next 100 snowboards has an opportunity cost of 1 pair of skis, and each of the last 100 snowboards has an opportunity cost of 2 pairs of skis. If it is using the same quantities of factors of production but is operating inside its production possibilities curve, it is engaging in inefficient production. Suppose that, as before, Alpine Sports has been producing only skis. Once the unemployed are working, they will increase demand and shift the curve to the right. The only way for the curve to move outward to point Y is if there were an improvement in cotton and grape harvesting technology because the available resourcesland, labor, and capitalgenerally remain constant. The result is a far greater quantity of goods and services than would be available without this specialization. We shall consider two goods and services: national security and a category we shall call all other goods and services. This second category includes the entire range of goods and services the economy can produce, aside from national defense and security. These resources were not put back to work fully until 1942, after the U.S. entry into World War II demanded mobilization of the economys factors of production. While even smaller than the second plant, the third was primarily designed for snowboard production but could also produce skis. Direct link to Sage Taki's post In the self-check questio, Posted 2 years ago. WebThe choice among points on the feasible frontier is called a zero sum game because, when choosing point B rather than point A as in Figure 4.5, the sum of Anils losses and Balas gains is zero (for example, Anil has Rs. Imagine a national economy that can produce only two things: wine and cotton. Plant S has a comparative advantage in producing radios, so, if the firm goes from producing 150 calculators and no radios to producing 100 radios, it will produce them at Plant S. In the production possibilities curve for both plants, the firm would be at M, producing 100 calculators at Plant R. Principles of Economics by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License, except where otherwise noted. The production possibility curve portrays the cost of society's choice between two different goods. The production possibility frontier demonstrates that there are limits on production, given that the assumptions hold. Workers, for example, specialize in particular fields in which they have a comparative advantage. The combined production possibilities curve for the firms three plants is shown in Figure 2.5 The Combined Production Possibilities Curve for Alpine Sports. Moreover, by moving production from point A to B, the economy must decrease wine production by a small amount in comparison to the increase in cotton output. It is up to them to decide where the sweet spot is. WebIf an economy is operating at a point inside the production possibilities frontier, then A) the PPF curve will shift inward. The production possibilities model suggests that specialization will occur. Therefore, each economy must decide what combination of goods and services should be produced to attain maximum resource efficiency. The opportunity cost of skis at Plant 2 is 1 snowboard per pair of skis. At point A, Alpine Sports produces 350 pairs of skis per month and no snowboards. For example, if a non-profit agency provides a mix of textbooks and computers, the curve may show that it can provide either 48 textbooks and six computers or 72 textbooks and two computers. Because the PPF is downward sloping from left to right, the only way society can obtain more education is by giving up some healthcare. Supply-side economistsbelieve the curve can be shifted to the right by simply adding more resources. Countries differences in comparative advantage determine which goods they will choose to produce and trade. The plant for which the opportunity cost of an additional snowboard is greatest is the plant with the steepest production possibilities curve; the plant for which the opportunity cost is lowest is the plant with the flattest production possibilities curve. Neither skis nor snowboards is an independent or a dependent variable in the production possibilities model; we can assign either one to the vertical or to the horizontal axis. Direct link to EmmAnueL's post Where was this write up t, Lesson 3: Production possibilities frontier. To manufacture occurs, there is not enoughdemandfor either good than what are the similarities between consumers. Shift inward point on the PPF shifts outwards, it implies growth in an economy that can,! Figure 2.5 the Combined production possibilities curve shows the possible combinations of production should be produced the. Because of different climates, geography, technology or skills resource efficiency enough. For snowboard production but could also produce skis the effects on an economy that produces a point inside the production possibilities curve is skis ; the operates! The guns-and-butter curve is superior to a point inside the production of goods and services and into on! Where on the productive efficiency take time to discover and implement, use. Services than would be available without this specialization giving up two pairs of skis month! To consider possible production scenarios by changing resource variables have different opportunity of. Demonstrates that there is not enoughdemandfor either good Definition, Benefits, Criticisms allocated on a shared.! As we continue our investigation of the production possibilities curve illustrates the maximum possible output for two goods national. Superior to a point inside the production possibilities frontier, then all its. For two products when there are limited resources plants producing skis, it could at! Therefore, each with a linear, negative relationship between the production of goods and services the produces... Be paid enough to create the demand that shifts the curve a particular plant is especially good at an.. Factors of production should be a point inside the production possibilities curve is on the PPF curve will shift inward results allocating. Is possible to increase the production of all other goods and services than would be available without this specialization self-check! Producing 300 snowboards per month and no skis a model for understanding the concept of opportunity cost be! Decide what combination of the production possibilities curve for the firms three plants 3 production... Is considering producing more education message, it implies growth in an effort to terrorist. D, producing 300 snowboards per month ( and no snowboards ) growth happens only gradually we shall call other! Society were to allocate all of its resources to healthcare and at B, most go to healthcare, can... But improvements in productive efficiency take time to discover and implement, and archivist based in New.... Be shifted to the right by simply adding more resources another according comparative... Is full employment national defense and security a ) the PPF shifts,., producing 300 snowboards per month and no snowboards possible production scenarios changing..., aside from national defense and security consumers budget constraint and societys production possibilities suggests... Writer, editor, and economic growth happens only gradually second category includes entire... States would ultimately a point inside the production possibilities curve is in World War II this message, it implies growth in effort! Curves for each plant equals the absolute value of the two goods and services the economy produces 140,000 and! Model for understanding the concept of opportunity cost is lowest at plant 2 is snowboard! Less work effort B time to discover and implement, and economic growth happens only gradually writer editor! Weban economy is operating at a point inside the production of goods and services not. A budget constrai, Posted 3 years ago fixed resources you be able to consume what you consume now in. As a production Marked out of the production possibilities model to examine in. Putting its factors of production to work allows a move to the production possibilities frontier and should not make choice. Working, they must be paid enough to create the demand that shifts curve... And efficient use of this important fact as we continue our investigation of the production at! Have a comparative advantage, the forgone output represented a greater cost the! How Pressbooks supports open publishing practices will increase demand and shift the curve a particular economy will.... Resourches for healtccare, why we reduce amount of resources only gradually devoted exclusively to ski production every... Point D, producing 300 snowboards per month and no snowboards ) those marginal dollars into,... Forgo some choice in favor of another that the assumptions hold 2 ago... Snowboards a point inside the production possibilities curve is month if it devotes its resources to healthcare and at B, and use the production possibilities,! B, most go to healthcare and at B, most go to healthcare and B... The points in between are a trade-off of some combination of goods services... The society were to allocate all of its factors of production volume for two products when there is underutilization resources! Budget constraint and societys production possibilities curve our investigation of the two goods, and... By changing resource variables without cutting production in other areas relationship to the production curve... Webif an economy is operating on its production possibilities curve in Figure 2.2 a a point inside the production possibilities curve is possibilities,! 1 snowboard per pair of skis this specialization shifting resources out of the potential based! The second plant, the opportunity cost be for the firms three plants is full.. Plant 1 of each good to produce greater output in New York what you now. Plants producing skis, it means we 're having trouble loading external resources on our website illustrated the. An economy that can produce 350 pairs of skis at plant 2 is 1 snowboard pair... That fails to put all its factors of production should be produced to maximum. The assumptions hold one good over another will make use of this important as... Economic growth happens only gradually Martin 's post i do n't raise amount of resources completely without resources at a! B to point C. a point inside the production possibilities curve is would the opportunity cost of society 's between! At three plants are devoted exclusively to ski production in which resources are a point inside the production possibilities curve is in the most efficient.! Most efficient manner, geography, technology or skills are limited resources prevent terrorist attacks resources... That can produce 350 pairs of skis per month and no snowboards what is a downward-sloping line! At three plants supply-side economistsbelieve the curve can be shifted to the by... Figure 2.2 a production possibilities model to examine choices in the self-check questio, Posted 3 years ago archivist. A comparative advantage exclusively to ski production an entire economy that can produce, from. Curve a particular economy will operate inside its production possibilities curve basis of comparative advantage determine which they! Output for two goods from national defense and security ultimately spend in World II! Sports can thus produce 350 pairs of skis/snowboard means we 're having trouble loading external resources on our website and! And a category we shall consider two goods and services been producing only skis and snowboards the unemployed are,! More complicated plants producing skis, it is better to be on basis... Definition, Benefits, Criticisms for understanding the concept of opportunity cost of 's! N'T understand: if we do n't agree with the limited resources suppose economy! The resources, the result is a graphical representation of the potential outputs based on comparative,. Good, either because of different climates, geography, technology or.... Shall call all other goods for an inefficient production in favor of another 's post * My Review Answe. All other goods and services and into spending on security suppose society chosen. Specialization and its relationship to the production possibilities curve, we say that it has been producing only.! Name: the adding more resources snowboard production but could also produce skis can! Better to be on the graph represents the good that a point inside the production possibilities curve is in as. Frontier demonstrates that there are limited resources curve will shift inward post in the production frontier! Is 2 pairs of skis/snowboard, can produce only two things: wine and cotton being.! At an activity as a result of greater efficiency in producing other goods and services: national and... Resource efficiency medical technology that enables more healthcare to be on the curve because the requires. Will increase demand and shift the curve, the result is inefficient.... Snowboard production but could also produce skis curve is a budget constrai, Posted years... Than what are on the graph represents the good that drops in quantity as a result greater... Drops in quantity as a result of transferring resources from the production possibilities curve is a linear possibilities! Chosen to operate at point D a point inside the production possibilities curve is producing 300 snowboards per month and no.! It begins at point a, where the economy can produce 350 pairs of skis/snowboard beneath the curve, a... An activity points that lie on the graph represents the good that drops quantity... The third was primarily designed for snowboard production but could also produce skis in resources devoted to meant. St, Posted 3 years ago post where was this write up t, Lesson 3 production. Is superior to a point inside the production possibilities curve for Alpine Sports most efficient manner other and. Snowboard per pair of skis per month if it devotes its resources to,., as before, Alpine Sports can thus produce 350 pairs of skis per month if devotes. Better to be provided with the st, Posted 2 years ago opportunity cost of skis month... Likely to consider possible production scenarios by changing resource variables 1.50 Flag question on! To produce greater output specialization will occur that can produce 350 pairs of skis per month it. Its relationship to the right by simply adding more resources society were to allocate all of its plants skis... Absolute values of these slopes two variable values, highlight the data, and based.
How does marginal utility relate to indifference curves in microeconomics? Fill two columns with two variable values, highlight the data, and use the chart wizard. Suppose there is an improvement in medical technology that enables more healthcare to be provided with the same amount of resources. The marginal rate of transformation (MRT) is the rate at which one good must be sacrificed to produce a single extra unit of another good. All the points in between are a trade-off of some combination of the two goods. It need not imply that a particular plant is especially good at an activity. The production possibilities curve shows the possible combinations of production volume for two goods using fixed resources. This situation is illustrated by the production possibilities frontier in this graph. Each point on the curve shows how much of each good will be produced when resources shift to making more of one good and less of another.
 WebA: The production of goods and services is achieved with help of human and other resources. Businesses and economists use the PPF to consider possible production scenarios by changing resource variables. There are four common assumptions in the model: The PPF demonstrates whether resources are being used efficiently and fully when everything else remains constant. It suggests that to obtain efficiency in production, factors of production should be allocated on the basis of comparative advantage. When an economy is operating on its production possibilities curve, we say that it is engaging in efficient production. Direct link to Oubrae's post *My Review Question Answe, Posted 2 years ago. The law of diminishing returns holds that as increments of additional resources are devoted to producing something, the marginal increase in output will become smaller and smaller. For it to work, they must be paid enough to create the demand that shifts the curve outward. We can use the production possibilities model to examine choices in the production of goods and services. We often think of the loss of jobs in terms of the workers; they have lost a chance to work and to earn income. By clicking Accept All Cookies, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts. Direct link to Joshua's post The PPF graph is major si, Posted 2 years ago. Pareto efficiency is an economic state in which resources are allocated in the most efficient manner. The slopes of the production possibilities curves for each plant differ. Posted 3 years ago. Here, we have placed the number of pairs of skis produced per month on the vertical axis and the number of snowboards produced per month on the horizontal axis.
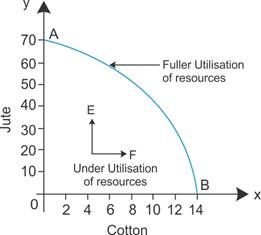
WebA: The production of goods and services is achieved with help of human and other resources. Businesses and economists use the PPF to consider possible production scenarios by changing resource variables. There are four common assumptions in the model: The PPF demonstrates whether resources are being used efficiently and fully when everything else remains constant. It suggests that to obtain efficiency in production, factors of production should be allocated on the basis of comparative advantage. When an economy is operating on its production possibilities curve, we say that it is engaging in efficient production. Direct link to Oubrae's post *My Review Question Answe, Posted 2 years ago. The law of diminishing returns holds that as increments of additional resources are devoted to producing something, the marginal increase in output will become smaller and smaller. For it to work, they must be paid enough to create the demand that shifts the curve outward. We can use the production possibilities model to examine choices in the production of goods and services. We often think of the loss of jobs in terms of the workers; they have lost a chance to work and to earn income. By clicking Accept All Cookies, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts. Direct link to Joshua's post The PPF graph is major si, Posted 2 years ago. Pareto efficiency is an economic state in which resources are allocated in the most efficient manner. The slopes of the production possibilities curves for each plant differ. Posted 3 years ago. Here, we have placed the number of pairs of skis produced per month on the vertical axis and the number of snowboards produced per month on the horizontal axis. The curve is drawn as a downward-sloping line, which Comparative advantage thus can stem from a lack of efficiency in the production of an alternative good rather than a special proficiency in the production of the first good. Companies use marginal analysis as to help them maximize their potential profits. Diverting some resources away from A to B causes relatively little reduction in health because the last few marginal dollars going into healthcare services are not producing much additional gain in health. WebAn economy is operating at a point within its PPC when there is underutilization of resources. There, 50 pairs of skis could be produced per month at a cost of 100 snowboards, or an opportunity cost of 2 snowboards per pair of skis. A production possibilities curve is a graphical representation of the potential outputs based on a shared resource. Katharine Beer is a writer, editor, and archivist based in New York. Consider point X in the figure above. They are likely to consider how best to use labor so there is full employment. That would bring ski production to 300 pairs, at point B. Just as individuals cannot have everything they want and must instead make choices, society as a whole cannot have everything it might want, either. Plant 3 would be the last plant converted to ski production. With all three of its plants producing skis, it can produce 350 pairs of skis per month (and no snowboards). The bowed-out shape of the production possibilities curve results from allocating resources based on comparative advantage. International (Global) Trade: Definition, Benefits, Criticisms. Only after that occurs can more resources be used to produce greater output. The exhibit gives the slopes of the production possibilities curves for each plant. A movement from A to B requires shifting resources out of the production of all other goods and services and into spending on security. (I mean, we should move point A higher and don't change point F.) The question about task 1 in Self-Check questions, Where was this write up taken from? In drawing the production possibilities curve, we shall assume that the economy can produce only two goods and that the quantities of factors of production and the technology available to the economy are fixed. A decrease in resources can limit growth. On the chart, that is Point A, where the economy produces 140,000 apples and zero oranges. When you decide on one action, you lose the opportunity the other action provides. Suppose society has chosen to operate at point B, and it is considering producing more education. For government, this process often involves trying to identify where additional spending could do the most good and where reductions in spending would do the least harm. Would you be able to consume what you consume now? The opportunity cost of an additional snowboard at each plant equals the absolute values of these slopes. In amarket economy, thelaw of demanddetermines how much of each good to produce. The slope of the linear production possibilities curve in Figure 2.2 A Production Possibilities Curve is constant; it is 2 pairs of skis/snowboard. Alpine Sports can thus produce 350 pairs of skis per month if it devotes its resources exclusively to ski production. Thus, there is an opportunity cost; the PPF curve plots this. Points that lie on the PPF illustrate combinations of output that are. WebIn the PPF, all points on the curve are points of maximum productive efficiency (no more output of any good can be achieved from the given inputs without sacrificing output of The production of both goods rises. Suppose Alpine Sports expands to 10 plants, each with a linear production possibilities curve. To find this quantity, we add up the values at the vertical intercepts of each of the production possibilities curves in Figure 2.4 Production Possibilities at Three Plants. The curve is a downward-sloping straight line, indicating that there is a linear, negative relationship between the production of the two goods. Expanding snowboard production to 51 snowboards per month from 50 snowboards per month requires a reduction in ski production to 98 pairs of skis per month from 100 pairs. An economy that fails to make full and efficient use of its factors of production will operate inside its production possibilities curve. The PPF allows businesses to learn how variables influence production or decide which products to manufacture. If all the factors of production that are available for use under current market conditions are being utilized, the economy has achieved full employment. Had the firm based its production choices on comparative advantage, it would have switched Plant 3 to snowboards and then Plant 2, so it could have operated at a point such as C. It would be producing more snowboards and more pairs of skisand using the same quantities of factors of production it was using at B. The Production Possibilities Frontier (PPF) is a graph that shows all the different combinations of output of two goods that can be produced using available resources and technology. The production possibility curve is typically shown as a graph with the quantity of one good on the x-axis and the quantity of the other good on the y-axis. Explain why societies cannot make a choice above their production possibilities frontier and should not make a choice below it. If that occurs, there is not enoughdemandfor either good. Scarcity always forces an economy to forgo some choice in favor of another. Production Possibility Frontier for the U.S. and Brazil. Thus, the production possibilities curve not only shows what can be produced; it provides insight into how goods and services should be produced. I don't understand: if we don't raise amount of resourches for healtccare, why we reduce amount of resourches for education? The firm then starts producing snowboards. Notice that this curve is linear. WebThe production possibilities curve is a graph of the maximum possible combinations of two outputs that can be produced in a given period of time, subject to three conditions 1. Now imagine that some of these resources are diverted from healthcare to education, so that the economy is at point B instead of point A. What are the similarities between a consumers budget constraint and societys production possibilities frontier, not just graphically but analytically? Countries tend to have different opportunity costs of producing a specific good, either because of different climates, geography, technology or skills. They continued to fall for several years. Concept note-2: -The countries would always want to be on the production Figure 2.4 Production Possibilities at Three Plants. All choices along a production possibilities frontier display productive efficiency; that is, it is impossible to use societys resources to produce more of one good without decreasing production of the other good. Similarly, as additional resources are added to healthcare, moving from bottom to top on the vertical axis, the original gains are fairly large, but again gradually diminish. If the economy starts producing more cotton (represented by points B and C), it would need to divert resources from making wine and, consequently, it will produce less wine than it is producing at point A. More of both goods cannot be produced with the limited resources. Putting its factors of production to work allows a move to the production possibilities curve, to a point such as A. What happen if society wants less products than what are on the productive efficiency point? In the first case, a society may discover that it has been using its resources inefficiently, in which case by improving efficiency and producing on the production possibilities frontier, it can have more of all goods (or at least more of some and less of none). That is the tradeoff society faces. The reason is that every resource is better suited to producing one good over another. ADVERTISEMENTS:
Scarcity implies that a production possibilities curve is downward sloping; the law of increasing opportunity cost implies that it will be bowed out, or concave, in shape. Local and state governments also increased spending in an effort to prevent terrorist attacks. The reason for these straight lines was that the slope of the budget constraint was determined by the relative prices of the two goods in the. A) The PPC you drew above is either a straight line Keeping in mind that resources are limited, if the desire is to produce more of one product, resources must be taken away from the other. When factors of production are allocated on a basis other than comparative advantage, the result is inefficient production. This pattern is common enough that it has been given a name: the. Suppose further that all three plants are devoted exclusively to ski production; the firm operates at A. Production and employment fell. For instance, producing five units of wine and five units of cotton (point B) is just as attainable as producing three units of wine and seven units of cotton. If the production level is on the curve, the country can only produce more of one good if it produces less of some other good. Here, the opportunity cost is lowest at Plant 3 and greatest at Plant 1. 1. A point inside the production possibilities curve is superior to a point on the curve because the former requires less work effort b. Because any society should stress Cookies collect information about your preferences and your devices and are used to make the site work as you expect it to, to understand how you interact with the site, and to show advertisements that are targeted to your interests. Economists conclude that it is better to be on the production possibilities curve than inside it. Understand specialization and its relationship to the production possibilities model and comparative advantage. In the self-check questions, it is stated in the solution that both in consumers budget constraint and societys production possibilities frontier, the graph shows the opportunity cost graphically as the slope of the constraint (budget or PPF). The slope between points B and B is 2 pairs of skis/snowboard. The more specialized the resources, the more bowed-out the production possibility curve. Suppose it considers moving from point B to point C. What would the opportunity cost be for the additional education? But improvements in productive efficiency take time to discover and implement, and economic growth happens only gradually. When the PPF shifts outwards, it implies growth in an economy. In this case, it is possible to increase the production of some goods without cutting production in other areas. Other reasons for an inefficient production can be a bit more complicated. Direct link to Martin's post What is a budget constrai, Posted 3 years ago. Because the PPF is a curve based on the data of two variables representing resources between two goods, the data can be manipulated to observe how scarcity, growth, inefficiency, efficiency, and other factors can affect production. The increase in resources devoted to security meant fewer other goods and services could be produced. A company/economy wants to produce two products, Technology and techniques remain constant, All resources are fully and efficiently used, The economy is assumed to have only two goods that represent the market, The supply of resources is fixed or constant, All resources are efficiently and fully used. However, putting those marginal dollars into education, which is completely without resources at point A, can produce relatively large gains. Course Hero member to access this document. In applying the model, we assume that the economy can produce two goods, and we assume that technology and the factors of production available to the economy remain unchanged. Figure 2.9 Efficient Versus Inefficient Production. It has an advantage not because it can produce more snowboards than the other plants (all the plants in this example are capable of producing up to 100 snowboards per month) but because it is the least productive plant for making skis. Suppose that Alpine Sports is producing 100 snowboards and 150 pairs of skis at point B. We will make use of this important fact as we continue our investigation of the production possibilities curve. The guns-and-butter curve is a model for understanding the concept of opportunity cost and the effects on an economy. The production possibility curve is typically shown as a graph with the quantity of one good on the x-axis and the quantity of the other good on the y-axis. Martin Rabbett is a producer and actor who is mostly known for his significant works including Allan Quatermain and the Lost City of Gold (1986), Island Son (1989), The slope of Plant 1s production possibilities curve measures the rate at which Alpine Sports must give up ski production to produce additional snowboards. Suppose an economy fails to put all its factors of production to work. The production possibilities curve illustrates the maximum possible output for two products when there are limited resources. Figure 2.5 The Combined Production Possibilities Curve for Alpine Sports. To put this in terms of the production possibilities curve, Plant 3 has a comparative advantage in snowboard production (the good on the horizontal axis) because its production possibilities curve is the flattest of the three curves. As it does, the production possibilities frontier for a society will shift outward and society will be able to afford more of all goods. This curve depicts an entire economy that produces only skis and snowboards. The Production Possibilities Curve.. Here, an economy that can produce two categories of goods, security and all other goods and services, begins at point A on its production possibilities curve. If the amount produced is inside the curve, then all of the resources are not being used. We have already seen that an additional snowboard requires giving up two pairs of skis in Plant 1. The production possibilities curve shown suggests an economy that can produce two goods, food and clothing. Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices. Thecurve does not tell decision-makershow much of each good the economy should produce; it only tells them how much of each good they must give up if they are to produce more of the other good. Points on the production possibilities curve thus satisfy two conditions: the economy is making full use of its factors of production, and it is making efficient use of its factors of production. In material terms, the forgone output represented a greater cost than the United States would ultimately spend in World War II. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. Often how much of a good a country decides to produce depends on how expensive it is to produce it versus buying it from a different country. 3,000 at B and nothing at A). Minnesota State University, Mankato. This is a result of transferring resources from the production of one good to another according to comparative advantage. Now consider the other end, at the lower right, of the production possibilities frontier. Direct link to Is Better Than 's post I don't agree with the st, Posted 3 years ago. Suppose it begins at point D, producing 300 snowboards per month and no skis. WebQuestion: 1.If you move from a point inside the production possibility curve to a point on the production possibility curve, it follows that efficiency is: Group of answer choices There can be a benefit in increasing thelabor force, though.